Page Not Found
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
A list of all the posts and pages found on the site. For you robots out there is an XML version available for digesting as well.
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
About me
This is a page not in th emain menu
Published:
This post will show up by default. To disable scheduling of future posts, edit config.yml and set future: false.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Some of the content and pictures in this article are excerpted from the CS-Notes. If there is infringement, please inform to delete
1. See more from the cheat sheet
| Command | Object | Description |
|---|---|---|
| git add | filename | Add files to the staging area |
| git commit -m | filename | Submit files in staging area to the repository |
| git commit –amend | Modify the last submission (use “shift+zz” to exit; use “q!” to exit without saving) | |
| git mv | original new | Modify the name of a file |
| git rm | filename | Delete files in both working directory and staging area (use “-f” to force delete) |
| git rm –cached | filename | Delete files in the staging area only |
| git pull | Fetch from and integrate with another repository or a local branch | |
| git push | Update remote refs along with associated objects | |
| git log | View submission logs | |
| git reflog | Show referentiable history versions | |
| git reset | version | Roll back the version to the staging area |
| git reset | HEAD~n | Move the HEAD pointer to the first “n” objects and roll back the objects to staging area |
| git reset –soft | HEAD~n | Move the HEAD pointer to the first “n” objects only |
| git reset –hard | HAED~n | Further restore the staging area files to working directory (overwrite the source code) |
| git diff | Compare files in working directory and staging area | |
| git diff | version | Compare files in working directory and repository |
| git diff | version1 version2 | Compare 2 files in a repository |
| git diff –cached | version | Compare files in staging area and repository (only files in repository have “version”) |
| git branch | branch name | Create a branch |
| git checkout | branch name | Switch to a branch |
| git merge | branch name | Merge changes from another branch |
| git branch -d | branch name | Delete a branch |
1. Git is a distributed version control system, while SVN is centralized

2. Comparison between centralized and distributed:
| Centralized | Distributed | |
|---|---|---|
| The copy of code | Only the central server | Everyone’s computer |
| Work without central server | × | √ |
| Networking required | √ | × |
| Create and merge | Slow (copy a complete code) | Fast |
1. The central server is used to exchange the changes of each user. Git can work without it, but the central server can run continuously which makes exchanges easier
1. After creating a new repository, the current directory becomes the workspace
2. There is a hidden directory “.git” in the workspace, which belongs to the Git version library

1. Implement

2. New

3. Commit

4. Merge

1. When two branches modify the same line of the same file, conflicts will occur during merging:

2. Git will use “<<<<<<<, =======, >>>>>>>” to identify contents of different branches. We only need to modify the conflicting parts to be the same to resolve the conflict
<<<<<<< HEAD
Creating a new branch is quick & simple.
=======
Creating a new branch is quick AND simple.
>>>>>>> feature1
1. After operating on a branch, switch to another branch before the changes are committed, the changes can also be seen on the other branch. This is because all branches share a same workspace
2. We can use git stash to store the changes of the current branch
$ git stash
Saved working directory and index state \ "WIP on master: 049d078 added the index file"
HEAD is now at 049d078 added the index file (To restore them type "git stash apply")
3. Stashing can be used to implement the “bug branch”
git stash to store the uncommitted changes of “dev branch”This article mainly records the problems & solutions I’ve met when operating Linux systems
1. For a specific instruction please refer to here
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| File Commands: | |
| ls | Directory listing |
| ls -al | Formatted listing with hidden files |
| ls -lt | Sort the Formatted listing by time modification |
| cd | Change to home directory |
| pwd | Show current working directory |
| mkdir dir | Create a directory dir |
| cat >file | Places the standard input into the file |
| more file | Output the contents of the file |
| tail -f file | Output the contents of file as it grows, starting with the last 10 lines |
| touch file | Create or update file |
| rm -r dir | Delete the directory recursively |
| rm -f file | Force to remove the file |
| rm -rf dir | Force to remove the directory dir |
| cp file1 file2 | Copy the contents of file1 to file2 |
| cp -r dir1 dir2 | Copy dir1 to dir2; create dir2 if not present |
| mv file1 file2 | Rename or move file1 to file2, if file2 is an existing directory |
| Process management: | |
| ps | To display the currently working processes |
| top | Display all running process |
| kill pid | Kill the process with given pid |
| killall proc | Kill all the process named proc |
| bg | List stopped or background jobs, resume a stopped job in the background |
| fg n | Brings job n to the foreground |
| Searching: | |
| grep pattern file | Search for pattern in file |
| grep -r pattern dir | Search recursively for pattern in dir |
| command | grep pattern | Search pattern in the output of another command |
| locate file | Find all instances of file |
| find . -name filename | Searches in the directory (represented by “.”) and below it, for files and directories with names starting with filename |
| pgrep pattern | Searches for all the named processes, that matches with the pattern and, by default, returns their ID |
| System Info: | |
| w | Display who is on line |
| whoami | Who you are logged in as |
| finger user | Display information about user |
| uname -a | Show kernel information |
| cat /proc/cpuinfo | CPU information |
| cat /proc/meminfo | Memory information |
| free | Show memory and swap usage |
| whereis app | Show possible locations of app |
| which app | Show which applications will be run by default |
| Compression: | |
| tar cf file.tar file | Create tar named file.tar containing file |
| tar xf file.tar | Extract the files from file.tar |
| tar czf file.tar.gz files | Create a tar with Gzip compression |
| tar xzf file.tar.gz | Extract a tar using Gzip |
| gzip file | Compresses file and renames it to file.gz |
| gzip -d file.gz | Decompresses file.gz back to file |
| Network: | |
| ping | Ping host and output results |
| whois domain | Get whois information for domains |
| dig domain | Get DNS information for domain |
| wget file | Download file |
| wget -c file | Continue a stopped download |
| Shortcuts: | |
| ctrl+z | Stops the current command, resume with fg in the foreground or bg in the background |
| ctrl+r | Type to bring up a recent command |
| Shutdown: | |
| shutdown -h | Shut down immediately after services are stopped |
| shutdown -r | Restart after services are stopped |
Vim is a popular and build-in text editor of Linux systems. In most of the cases I use it to modify configuration files of networking or apps
1. Three modes

2. Commands in the bottom-line mode
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| :w | Write to disk |
| :w! | Force writing to disk when the file is read-only |
| :q | Leave |
| :q! | Force leaving without saving |
| :wq | Leave after writing to disk |
| :wq! | Leave after forcing writing to disk |
In case we have to construct a network includes Linux systems, usually we have to config static IP addresses for them. Here I use “Ubuntu 18.04” as an example (configurations on “CentOS” and “Fedora” are similar)
1. System UI
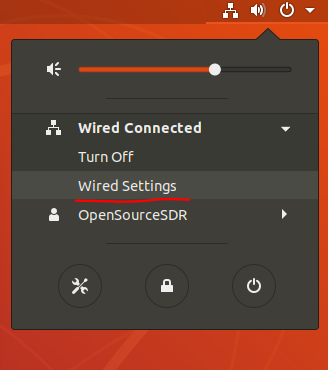

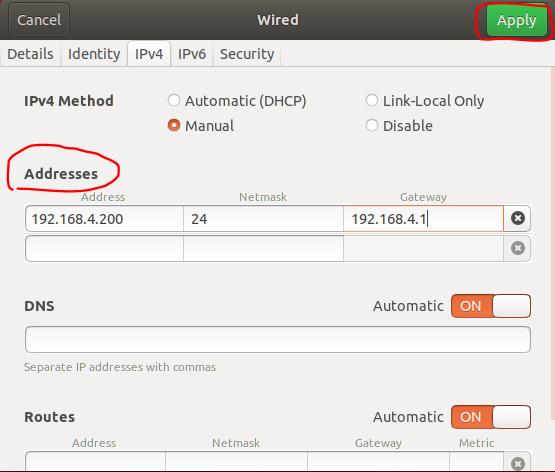
2. CommandLine
ifconfig to check the name of targeted network card
sudo vi /etc/network/interfaces or sudo gedit /etc/network/interfaces to open the configuration file
auto ens33
iface ens33 inet static
address 192.168.4.200
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.4.1

/etc/init.d/networking restart
sudo service network-manager restart
sudo service networking restart
1. Problem
2. Rationale
3. Solution1
sudo chmod 777 /var/log/syslog . It does work at first, nevertheless, I find that the permission of “syslog” will turn back to read-only each time I restart the system4. Solution2
sudo gedit /etc/passwd we can not only grant apps but also users. To do this, simply change the corresponding number after the “x:” to “0”
1. Problem
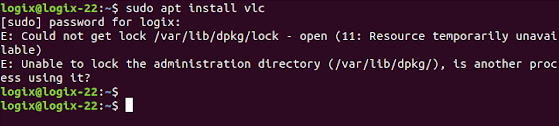
2. Rationale
3. Solution
ps -e | grep apt to find out related processessudo kill PID to terminate processes if returnedsudo rm /var/lib/apt/lists/lock
sudo rm /var/cache/apt/archives/lock
sudo rm /var/lib/dpkg/lock
1. At first, I practiced my online programming on the well-known Leetcode. However, I found some paid functions on Leetcode, such as Debug and spell check, are free on Nowcoder, so I mainly use Nowcoder to train my programming now
2. The reason why I choose C for online programming is that C is relatively rudimentary and does not have many powerful built-in functions that Python and C++ have. So programming with C allows me to have a more comprehensive and in-depth understanding of data structure & algorithm
1. Using macro definition to realize exchange: #define swap (x,y,t) (t = x, x = y, y = t)
2. Solution:
int count=0;
char *tmp, *rec;
char *out[];
void dfs(char* s, int i, int len){
if (i == len) { // End condition
strcpy(out[count++],tmp);
return;
}
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
if (j > 0 && s[j] == s[j - 1] && rec[j - 1] == 0)
continue; // Sorting can put the same numbers together so that you can skip them here
if (rec[j] == 0) {
rec[j] = 1;
tmp[i] = s[j];
dfs(s, i + 1, len);
rec[j] = 0;
}
}
}
int main(){
…
scanf("%s",s);
qsort(s,strlen(s),sizeof(char),cmp); // Sorting is the key! The "cmp" function is omitted here
dfs(s,0,strlen(s));
…
}
1. A template for such problem:
void dfs(int n, int m){
maze[n][m]=1; // Mark this position has been passed
k++;
if(n==row-1 && m==col-1){ // End condition
…;
return;
}
if(n+1<row && !maze[n+1][m]) dfs(n+1,m);
if(m+1<col && !maze[n][m+1]) dfs(n,m+1);
if(n-1>=0 && !maze[n-1][m]) dfs(n-1,m);
if(m-1>=0 && !maze[n][m-1]) dfs(n,m-1);
k--;
maze[n][m]=0; // Restore step and mark (Whether backtracking is needed depends on the actual situation)
}
2. If the entrance is not unique, use for loops (usually 2) in the main func to traverse all the entrances.
1. Use array “rec” to mark whether the number has been used, to further achieve the full arrangement:
for(int j=0;j<4;j++){
if(rec[j]==0){
rec[j]=1;
//dfs(in,i+1,calc);
dfs(in,i+1,calc+in[j]);
dfs(in,i+1,calc-in[j]);
dfs(in,i+1,calc*in[j]);
dfs(in,i+1,calc/in[j]);
rec[j]=0;
}
}
2. The end condition for the requirement to output the formula: (“i” starts from 0)
char* formu[9]; // Because input has the value of 10, a two-dimensional array is needed
if (i == 4) {
if (calc == 24) {
if (!strcmp(formu[0], "+")) { // Elements in array are no longer "char" but "string"
flag = 1;
for (int l = 1; l < k; l++) { // Skip the first operator
printf("%s", formu[l]);
}
}
}
return;
}
1. A confusible point in C:
2. Solution:
bool match(char* str, char* str1) {
if (*str == '\0' && *str1 == '\0') // End at the same time, return true
return true;
if (*str == '\0' || *str1 == '\0') // One ends first, return false
return false;
if (*str == *str1 || abs(*str - *str1) == 32) {
return match(str + 1, str1 + 1);
}
else if (*str == '?' && (isdigit(*str1) || isalpha(*str1))){
return match(str + 1, str1 + 1);
}
else if (*str == '*' && (isdigit(*str1) || isalpha(*str1))) {
while (*str == '*') { // Multiple "*" are equivalent to one "*"
str++;
}
str--;
return match(str + 1, str1) || match(str + 1, str1 + 1) || match(str, str1 + 1);
// 0 matched: str+1, str1 fixed; 1 matched: str+1, str1+1; Multiple matched: str fixed, str+1
}
return false;
}
1. Solution:
int i;
int calc(char* in, int len) {
char flag = '+';
int stack[40];
int tmp = 0, out = 0, top=-1;
while (i < len) {
tmp = 0;
if(in[i]=='-')
flag=in[i++];
if (in[i] == '{' || in[i] == '[' || in[i] == '('){
i++;
tmp = calc(in, len);
}
while (in[i] >= '0' && in[i] <= '9') {
tmp = tmp * 10 + in[i] - '0';
i++;
}
switch (flag) {
case '+': stack[++top] = tmp; break;
case '-': stack[++top] = -tmp; break;
case '*': stack[top] *= tmp; break;
case '/': stack[top] /= tmp; break;
}
if (in[i] == '}' || in[i] == ']' || in[i] == ')') {
i++;
break;
}
flag = in[i++];
}
for (int j = 0; j <= top; j++) {
out += stack[j];
}
return out;
}
Description: For example, 8/11 = 1/2 + 1/5 + 1/55 + 1/110
1. Solution:
while(scanf("%lld%c%lld", &fz, &slash, &fm)!=EOF){ // Use "scanf" to directly change "char" into "int"
while(fz!=1){
if(fm%fz==0){
fm/=fz;
break;
}
long long x=fm/fz;
long long y=fm%fz;
printf("1/%lld+",x+1);
fz-=y;
fm*=x+1;
}
printf("1/%lld\n",fm);
}
1. Output the float variable with specified number of decimals, like 2: printf("%.2f", i);
1. Find the greatest common divisor of “a” and “b”: int gcd(int a, int b){ return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b); }
2. The least common multiple: (a*b) / gcd(a,b)
Description: For example, when the length of the rope is 8, we cut it into three sections with lengths of 2, 3, 3 to get the maximum product 18
1. “N” divided by “M” and rounded up: int res = (N - 1) / M + 1;
1. Solution:
char* minWindow(char* S, char* T ) {
int lens=strlen(S), lent=strlen(T), out=lens+1, l=0, r=0, k=0;
char* hash=calloc(128, sizeof(char));
for(int i=0;i<lent;i++){
hash[T[i]]++;
}
while(r<lens){
if(hash[S[r]]>0)
lent--; // 1 matched
hash[S[r]]--;
r++;
while(!lent){ // All matched, narrow the left bound (at this time in "hash", only values of the characters to be matched are 0, others are negative)
if(out>r-l){
out=r-l; // Record length "r-l" and start position "l" of the substring
k=l;
}
if(map[S[l]]==0)
lent++; // This is an element that needs to be included, which means narrowing is completed. So we can end the "while(!lent)"
hash[S[l]]++;
l++;
}
}
if(out==lens+1) // Matching is incomplete
return "";
S[k+out]='\0'; // End the string and prepare for the "return"
return &S[k];
}
Description: Define the sibling of a word as a word that can be generated by exchanging the letters in the word any times but without adding, deleting or modifying letters
1. By judging whether a value in hash is zero after “++” and “–”, you can know whether all elements of two strings with different orders are the same:
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
hash[word[i]]++;
hash[sample[i]]--;
}
1. Solution: Merge sort
static long P = 0;
static int tmp[100000];
void merge(int* arr, int* tmp, int l, int mid, int r) {
int ll = l, rr = mid + 1, k = 0;
while (ll <= mid && rr <= r) {
if (arr[ll] < arr[rr])
tmp[k++] = arr[ll++];
else {
P += (mid - ll + 1);
P %= 1000000007; // Surely these 2 steps are not needed in the normal template of merge sort
tmp[k++] = arr[rr++];
}
}
while (ll <= mid) {
tmp[k++] = arr[ll++];
}
while (rr <= r) {
tmp[k++] = arr[rr++];
}
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++){
arr[i] = *(tmp++); // Array "data" pointed by the formal parameter pointer "arr" will change accordingly
}
}
void mergesort(int* arr, int l, int r) {
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (l < r) {
mergesort(arr, l, mid);
mergesort(arr, mid + 1, r);
merge(arr, tmp, l, mid, r);
}
}
int InversePairs(int* data, int dataLen ) {
mergesort(data, 0, dataLen - 1);
return P;
}
Description: Find all triples in an array that meet “a+b+c=0”
1. Solution:
int** threeSum(int* num, int numLen) {
qsort(num, numLen, sizeof(int), cmp);
int** arr = calloc(300, sizeof(int*));
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numLen - 2; i++) {
int *pre = &num[i+1], *end = &num[numLen - 1];
while (pre < end) {
if (num[i] + *pre + *end == 0) {
arr[k] = calloc(3, sizeof(int));
arr[k][0] = num[i];
arr[k][1] = *pre;
arr[k][2] = *end;
k++;
while (*pre == *(pre + 1))
pre++;
pre++;
while (*end == *(end - 1))
end--;
end--;
}
else if (num[i] + *pre + *end > 0)
end--;
else
pre++;
}
while (num[i] == num[i+1])
i++;
}
return arr;
}
1. Extract letters from a string in alphabetical order (case-insensitive) and put them into a new array:
for (char j = 'A'; j <= 'Z'; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(input); i++) {
if (input[i] == j || input[i] - 32 == j)
character[index++] = input[i];
}
}
Description: There are 3 kinds of goods: main part, accessory 1 and 2, accessories must be purchased after the corresponding main part. Known the price and satisfaction of each product, calculate the maximum satisfaction we can get with money N
1. Store the price and satisfaction of accessories and main parts into the corresponding 2D array (q is the number of corresponding main part):
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int v, p, q;
scanf("%d %d %d", &v, &p, &q);
if (!q) { // main part
val[i][0] = v; wei[i][0] = v * p;
}
else if (val[q][1] == 0) { // accessory 1
val[q][1] = v; wei[q][1] = v * p;
}
else { // accessory 2
val[q][2] = v; wei[q][2] = v * p;
}
}
2. 4 cases of state transfer:
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = N; j >= 0; j--) {
if (val[i][0] <= j) {
dp[j] = Max(dp[j],
wei[i][0] + dp[j - val[i][0]]); // Buy this one "wei[i][0]+dp[j-val[i][0]]" or not "dp[j]"
}
if (val[i][1] && (val[i][0] + val[i][1]) <= j) {
dp[j] = Max(dp[j],
wei[i][0] + wei[i][1] + dp[j - val[i][0] - val[i][1]]);
}
if (val[i][2] && (val[i][0] + val[i][2]) <= j) {
dp[j] = Max(dp[j],
wei[i][0] + wei[i][2] + dp[j - val[i][0] - val[i][2]]);
}
if (val[i][2] && (val[i][0] + val[i][1] + val[i][2]) <= j) {
dp[j] = Max(dp[j],
wei[i][0] + wei[i][1] + wei[i][2] + dp[j - val[i][0] - val[i][1] - val[i][2]]);
}
}
}
Description: Calculate the minimum number of people to leave to form a mountain shaped (eg. 1 3 6 3 2) height formation in a team with N members
1. Solution: Take “i” as the center to find the longest ascending subsequence on both sides from → and ← respectively:
int chorus(int *h, int N) {
int max = 0;
int l[N], r[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
l[i]=1; r[i]=1;
}
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (h[j] < h[i] && l[i] < l[j] + 1)
l[i] = l[j] + 1;
}
}
for (int i = N-2; i >=0; i--) {
for (int j = N-1; j > i; j--) {
if (h[j] < h[i] && r[i] < r[j] + 1)
r[i] = r[j] + 1;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
int tmp=r[i]+l[i]-1; // Notice the central person "i" was counted twice
if(tmp>max)
max=tmp;
}
printf("%d\n",(N-max));
return 0;
}
Description: Get the longest palindrome substring
1. Solution: Traverse all values of length through “i”. If string[j-k] is a palindrome, set dp[j][k] to 1
2. 3 cases of state transfer:
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
for(int j=0;j<len-i;j++){
int k=j+i;
if(!i)
dp[j][k]=1;
else if (i==1 && in[j]==in[k])
dp[j][k]=1;
else if(dp[j+1][k-1] && in[j]==in[k])
dp[j][k]=1;
if(dp[j][k])
max=fmax(max, i+1); // length = i+1
}
}
1. Develop the habit of using a null node to indicate the linked list (In case the first and last node need to be reversed)
2. Solution: The position of “pre” and “cur” actually don’t change, and constantly insert “new” between “pre” and “cur”
while(n-m){
new=cur->next;
cur->next=new->next;
new->next=pre->next;
pre->next=new;
n--;
}
1. Solution: The fast pointer moves n steps first, then the slow pointer starts. When the fast pointer points to NULL, the slow pointer points to the nth node from the bottom of the linked list.
1. Definition of the node:
typedef struct LinkNode{
int val;
struct LinkNode* next;
}LinkNode;
2. Create a node: LinkNode* p=malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
3. If the head node of the linked list is unknown, use the value of targeted node’s next node to cover the value of targeted node, and then remove its next node
1. It is a variation of preorder traversal, that is, the results of preorder traversal are stored hierarchically
static int k=0;
void levelorder(struct TreeNode* root, int level, int** out, int* arrlevel){ // Recursive parameters need to include the current level of the tree
if(root == NULL)
return;
if(level>=k){
out[level]=calloc(1000,sizeof(int)); // The output array also becomes two-dimensional
k++;
}
out[level][arrlevel[level]++]=root->val;
levelorder(root->left, level+1, out, arrlevel);
levelorder(root->right, level+1, out, arrlevel);
}
1. Calculate the depth of a tree:
int depth(TreeNode *root) {
if (!root)
return 0;
int ldep = depth(root->left);
int rdep = depth(root->right);
return fmax(ldep, rdep) + 1;
}
1. Solution:
struct TreeNode* recur(int* xianxu, int* zhongxu, int Len){
if(!Len)
return NULL;
struct TreeNode* out=calloc(Len, sizeof(struct TreeNode));
out->val=xianxu[0];
int i=0;
for(;i<Len;i++){
if(zhongxu[i]==xianxu[0])
break;
}
int newxxl[i+1], newxxr[Len-i], newzxl[i+1], newzxr[Len-i];
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
newxxl[j]=xianxu[j+1];
newzxl[j]=zhongxu[j];
}
for(int j=0;j+i+1<Len;j++){
newxxr[j]=xianxu[j+i+1];
newzxr[j]=zhongxu[j+i+1];
}
out->left=recur(newxxl, newzxl, i);
out->right=recur(newxxr, newzxr, Len-i-1);
return out;
}
1. The queue is quite suitable for the maintenance of sliding window (A queue actually is an array with 2 pointers)
2. Definition of the queue:
typedef struct queue{
int data[MAX];
int head;
int tail;
}Queue;
3. Create a queue: Queue q;
1. Tips of switch():
case 'a': // It will execute the same as the next "case"
case 'A': in[i]='5'; break;
1. Convert decimal to binary (8-bit):
void DeciToBina(int n, int* out) {
int length=0;
int a[8];
while (n>0) {
a[length++] = (n % 2);
n = n / 2;
}
while(length<8){
a[length++]=0; // Fill with "0"
}
for (int i = length - 1, k=0; i >= 0; i--){
out[k++] = a[i]; // Output the remainders in reverse order
}
}
2. Convert IP address to binary (32-bit):
void IPToBina(char* in, int* out){
int tmp=0, count=0, c=0;
int* ip[4];
for(int j=0;j<=strlen(in);j++){
if(in[j]!='.' && isdigit(in[j]))
tmp=tmp*10 + in[j]-'0';
else if(in[j]=='.' || j==strlen(in)){
ip[count]=calloc(8, sizeof(int));
DeciToBina(tmp, ip[count++]);
tmp=0;
}
}
for(int a=0;a<4;a++){
for(int b=0;b<8;b++){
out[c++]= ip[a][b];
}
}
}
Description: Enter a line of positive integers to be pushed, output all schemes of popping in dictionary order
1. Dictionary order: Achieved by qsort and strcmp
return strcmp((char*)a, (char*)b);return strcmp(*(char**)a, *(char**)b);1. Tips: Use getchar() to drop a unneeded character from the input
1. Treat the complement of a negative number as the true form to obtain its corresponding positive number:
unsigned int tmp = (unsigned int) n;
1. PHP files can include “html”, “CSS” and “JavaScript” code
2. Basic symbols
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
<?php ... ?> | Tags for PHP code |
; {} | Statement terminators |
// /*...*/ | Annotations |
$s | Define a variable “s” |
= | Assignment Operator |
1. PHP use echo and print to output contents:
<?php
echo 111,222; // Multiple
echo '<hr>';
print 111; // Single
echo '<hr>';
$a_zzy = 'Variable name cannot begin with a number and there cannot be spaces after the $';
echo $a_zzy;
?>
1. Integer, float, boolean, null and string
<?php
$x = true;
var_dump($x); // "var_dump()" can print the type of a variable
$y = -123;
var_dump($y);
$f = 3.1415;
var_dump($f);
$s1 = '我是'; // The length of 1 Chinese character == 3 en characters
var_dump($s1);
$s2 = 'my name is Jay';
var_dump($s2);
$s3 = "$s1 zzy"; // " can parse variable content, while ' cannot
var_dump($s3);
$n = null;
var_dump($n);
?>
2. Array
<?php
$arr1 = array( // Or use "[]"
'ouyang',
'miejue'
);
echo $arr1[1],'<hr>';
$arr2 = [
'ouyang' => '欧阳',
'西门吹雪',
'东方不败'
];
echo $arr2['ouyang'],'<hr>'; // Custom array subscript
print_r($arr2); // Output the whole array
echo '<hr>';
$s1 = 'I am';
echo $s1.$arr1[1], '她叫', $arr2[1]; // "." and "," have the same effect
3. Multidimensional array (Try not to exceed 3 dimensions)
$MultiD_arr = array(
array(
'ouyang'
),
array(
'miejue'
),
array(
'ximen',
'kungfu'=>[
'PHP',
'Python',
'C++']
)
);
print_r($MultiD_arr); // Arrays of different dimensions can be nested together
echo '<hr>';
echo 'I can use'.$MultiD_arr[2]['kungfu'][1].', and am learning'.$MultiD_arr[2]['kungfu'][0]; // Access elements in multi-D array
4. Loops in array
foreach($arr2 as $k=>$v){ // Key "k" and value "v"
echo $v, $k;
echo '<hr>';
}
foreach($MultiD_arr as $k=>$v){ // It proves that we'd better not to define a mixed-dimensional array
foreach($v as $vv){
echo $vv;
}
}
?>
5. Constant
<?php
define('HOST', '127.0.0.1'); // Definition method 1
echo HOST;
const NAME = 'PHP website'; // Definition method 2
echo NAME;
?>
1. Conditional statements
<?php
// "?" and ":"
$str1 = 'ouyang';
echo $str1 ? 'I am ouyang' : 'Unknown';
// "if", "elseif" and "else"
$str2 = '';
$str3 = '1';
if($str2){
echo 'I have content';
}
elseif($str3){
echo "I have".$str3;
}
else{
echo 'Both are null';
}
// "switch"
switch($str1){
case 'ouyang':
echo 'I am ouyang';
break;
case 'miejue':
echo 'I am miejue';
break;
default:
echo $str1;
}
// PHP8 has "match()" to match and output in the form of key&value
$str4 = 'zzy';
echo match($str4){ // Exact match (while "switch" is not). For example, character number and integer number will be distinguished
'hht' => 'Haotian He',
'zzy' => 'Zhongyi Zheng',
'wj' => 'Jing Wang'
};
?>
2. Built-in functions
<?php
$ouyang = 'OUYANG';
echo strtolower($ouyang); // Convert to lowercase
$miejue = 'miejueshitai';
echo strtoupper($miejue); // Convert to uppercase
$php = 'ouyang, miejue, ximen';
print_r ( explode(',', $php) ); // Divide string into array by ","
$ximen = 'ximen';
echo md5($ximen); // Use "md5" to encrypt string
$arr = ['ouyang', 'ximen', 'tianpeng'];
echo count($arr); // Counting the number of elements
echo implode(',',$arr); // Combine array into string by ","
echo in_array('tianpeng', $arr); // Query the giving content
array_pop($arr); // Delete the last element
print_r($arr);
?>
3. Custom functions
<?php
$num2 = 13;
function num($num1, $num2){
//global $num2; //Use "global" to call global variables in functions
return $num1 * $num2;
}
echo num(12, 11);
?>
4. Operators
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| + | Add |
| - | Subtract |
| * | Multiply |
| / | Divide |
| % | Modular |
| ++ | Same as in C |
| – | Same as in C |
| == | Equal to |
| != | Not equal to |
| >= | Greater than or equal to |
| <= | less than or equal to |
| === | Identically equal to |
| !== | Not identically equal to |
| and | Logic and |
| or | Logic or |
| xor | Logic xor |
| ! | Logic not |
<?php
var_dump( 100 === 100 );
echo '<hr>';
var_dump( true === 'true' ); // "(Not) Identically equal to" compare not only values but also data types
?>
5. Loops
<?php
// "while"
$int = 1;
while($int < 10){
echo $int;
$int++;
}
// "do...while"
$int = 1;
do {
echo $int;
$int++;
}while($int < 10);
// "for"
$int1 = 1;
for($int1; $int1<10; $int1++){
if($int1 == 5){
echo '5';
}
else{
echo $int1;
}
}
?>
1. PHP could operate databases through the “PDO (PHP Data Object)”:
<?php
$pdo = new PDO('mysql:host=localhost;dbname=blog', 'root', 'root'); // PDO($dsn, $username, $password)
//var_dump($pdo);
$stmt = $pdo->prepare('select * from article'); // "->" calls the property of the class
$stmt->execute();
$arr = $stmt->fetchAll();
print_r($arr);
?>
2. Instruction about the Mysql database please refer to here
1. Use
| Superglobal variable | Description |
|---|---|
$_GET | Receive the value in the URL, which is displayed after “?” |
$_POST | Receive the value in the URL, but not be displayed |
$_COOKIE | Be used to identify users and stored in client browsers |
$_SESSION | Be used to store “sessions” and stored in servers |
$_REQUEST | Include the value of “get”, “post” and “cookie” |
$GLOBALS | A global combined array that includes all variables |
2. Example
<?php
// print_r($GLOBALS);
setcookie('user','admin');
print_r($_COOKIE);
echo '<hr>';
session_save_path("D:/");
session_start();
$_SESSION['user'] = 'admin';
print_r($_SESSION);
?>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>PHP website</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="post">
lecturer: <input type="text" name="name" /> School:
<input type="text" name="school" />
<input type="submit" value="submit" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
1. Three characteristics:
2. Class attribute and class method
<?php
class Teacher{
// Class attribute (variable)
public $name = 'ouyang'; // "public" (default): visible within class, outside class and in subclasses
protected $school = 'SWJTU'; // "protected": visible within class and subclasses, but invisible outside class
private $id_num; // "private": visible only within class, invisible in subclasses and outside class
// Method
public function fun1(){
echo 'Name:miejue, School: SCU<hr/>'; // Try not to use "echo" but "return" in class
}
public function fun2(){
return 'Name:miejue, School: SCU<hr/>';
}
public function fun3(){ // Use pseudo variable "$this" to refer to the variable of current class
return 'Name:'.$this->name.', School: '.$this->school.', ID Number: '.$this->id_num.'<hr/>';
}
public function fun4(){
return $this->fun3(); // Use pseudo variable "$this" to refer to the method of current class
}
// Magic methods (Only record "__construct" and "__destruct" here)
public function __construct($name, $school, $id_num){ // "__construct" is executed when instantiating
$this->name = $name;
$this->school = $school;
$this->id_num = $id_num;
}
public function __destruct(){ // "__destruct" is automatically executed after the class execution
echo 'Class executed, ready to be destructed<hr/>';
}
}
3. Inheritance and polymorphism
class PHPteacher extends Teacher{ // Inherit the class "Teacher" defined above
public function fun5(){
return $this->school;
}
public function fun6(){
return $this->id_num;
}
public function fun1(){
return 'I am rewritten here to embody the Polymorphism<hr/>';
}
}
// Some tests
$ximen = new Teacher('ximen','SCU','5101061998');
print_r($ximen);
echo '<hr/>';
echo $ximen->name;
echo '<hr/>';
echo $ximen->fun3();
$ouyang = new PHPteacher('ouyang','SWJTU','5101051997');
print_r($ouyang);
echo '<hr/>';
echo $ouyang->id_num; // Cannot access "id_num" (private)
echo '<hr/>';
echo $ouyang->fun5(); // Can access "school" (protected)
echo $ouyang->fun6(); // Still cannot access "id_num"
echo $ouyang->fun3();
echo $ouyang->fun1();
?>
4. Abstract class
<?php
abstract class Teacher1 { // Notice that there is no "abstract attribute"
protected $name;
private $school;
public function __construct($name, $school) {
$this->name = $name;
$this->school = $school;
}
public function fun1() {
return 'Name: ' . $this->name . ', School: ' . $this->school .'<hr/>';
}
abstract public function fun2();
}
class PHPTeacher1 extends Teacher1 {
public function fun3() {
return $this->fun1();
}
public function fun2() {
return 'I am the rewritten method after inheriting <hr/>';
}
}
$obj = new PHPTeacher1('ximen', 'SCU');
echo $obj->fun2();
echo $obj->fun3();
?>
5. Interface
<?php
interface file{
public function noTF($param); // Don't need to use the "abstract" keyword, but end its methods with ";"
public function noZY($param);
}
class Teacher2 implements file { // Use "implements" to implement an interface
protected $name;
private $school;
public $noTF;
public $noZY;
public function __construct($name, $school) {
$this->name = $name;
$this->school = $school;
}
public function noTF($param) {
$this->noTF = $param;
}
public function noZY($param) {
$this->noZY = $param;
}
public function fun1() {
return 'I am' . $this->name . ', ' . $this->noTF . $this->noZY;
}
}
$obj = new Teacher2('ouyang', 'SWJTU');
$obj->noTF('I didn't conduct corporal punishment on students, ');
$obj->noZY('I didn't assign any homework');
echo $obj->fun1();
?>
6. Namespace
<?php
namespace one;
const NAME = 'Constant of miejue <hr/>';
function php(){
return 'Function of miejue <hr/>';
}
class phpcn{
public function fun(){
return 'Class of miejue <hr/>';
}
}
// Access in namespace one
echo php();
echo \two\php();
echo \one\three\php();
use \one\three as t; // Use sub-namspace "one\three" and rename it with "as"
echo t\php();
namespace two;
const NAME = 'Constant of ximen <hr/>';
function php(){
return 'Function of ximen <hr/>';
}
class phpcn{
public function fun(){
return 'Class of ximen <hr/>';
}
}
namespace one\three; // Sub-namespace
const NAME = 'Constant of ouyang <hr/>';
function php(){
return 'Function of ouyang <hr/>';
}
class phpcn{
public function fun(){
return 'Class of ouyang <hr/>';
}
}
?>
New feature 1: JIT compiler
New feature 2: You can assign variables with default values when calling functions
function test($a,$b=0,$c=0,$d=0){
echo $a;
echo '<hr/>';
echo $b;
echo '<hr/>';
echo $c;
echo '<hr/>';
echo $d;
}
test(10,20,30,40);
function test($a,$b=0,$c=0,$d=0){
echo $a;
echo '<hr/>';
echo $b;
echo '<hr/>';
echo $c;
echo '<hr/>';
echo $d;
}
test(10,20,d:30,c:40);
New feature 3: You can define and initialize attributes in the constructor at the same time
public function __construct(public $name, public $school, public $id_num){}
Short description of portfolio item number 1
Short description of portfolio item number 2 
Published:
Student Research Training Program(SRTP) of Southwest Jiaotong University [grant 180440]
Published:
Applied Basic Research Project of Science & Technology Department of Sichuan Province [grant 21YYJC3147]
Published:
This vulnerability has been submitted to China National Vulnerability Database of Information Security, numbered: CNNVD-202204-3571
Zhongyi Zheng, Saifei Li, Xiong Deng, Lianshan Yan
Download here
Published:
This is a description of your talk, which is a markdown files that can be all markdown-ified like any other post. Yay markdown!
Published:
This is a description of your conference proceedings talk, note the different field in type. You can put anything in this field.
Undergraduate course, University 1, Department, 2014
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.
Workshop, University 1, Department, 2015
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.